GPIO and Python (7/9) - Temperature Sensor
In this project you will learn how to wire and program a temperature sensor. Let’s see how hot the room is.
Things you will need:
Raspberry Pi + SD Card
Keyboard + Mouse
Monitor + HDMI Cable
Power Supply
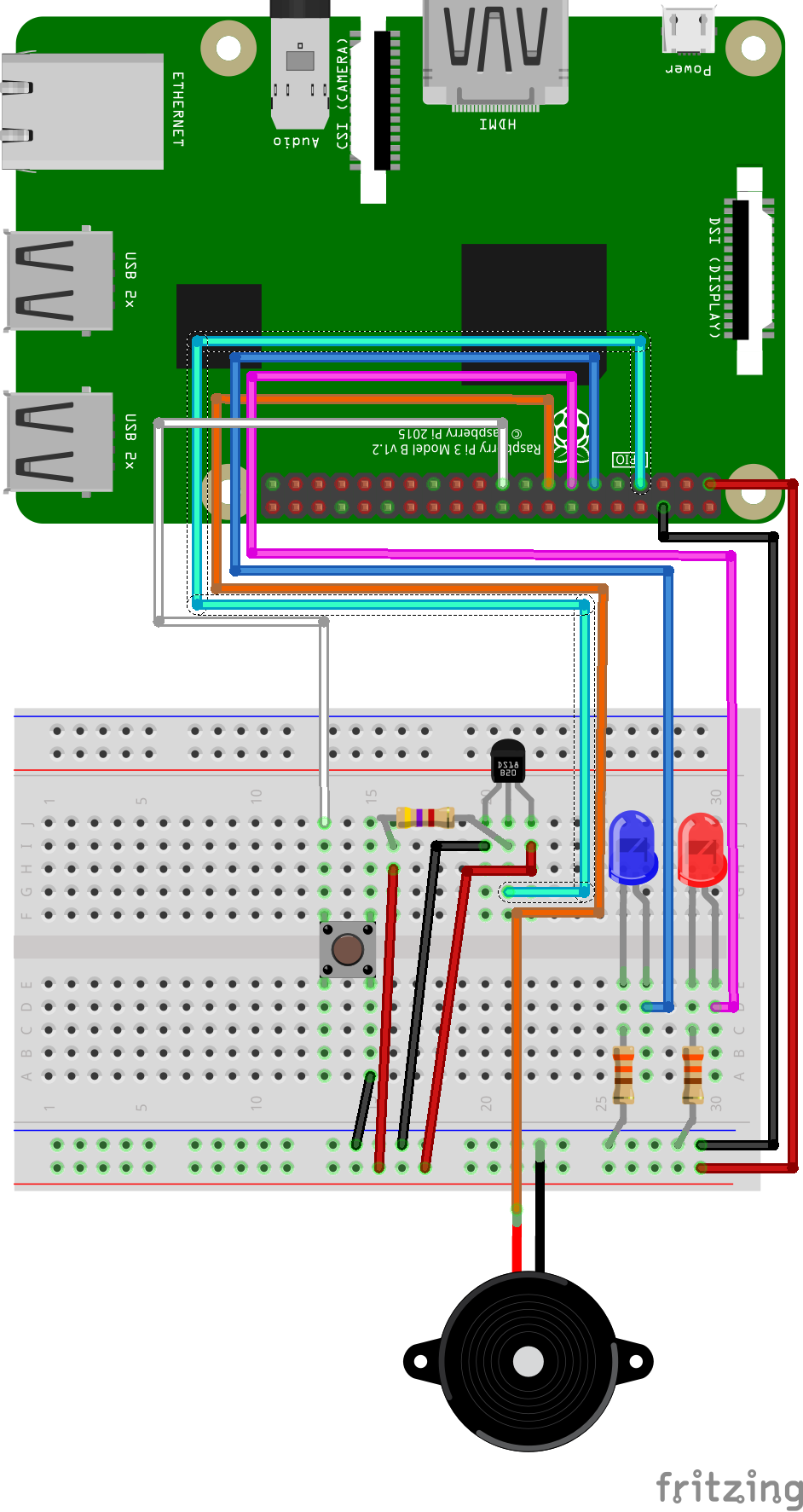
Breadboard
1x Red LED
1x Blue LED
2x 330? Resistor
5x M/M Jumper Wire
7x M/F Jumper Wire
1x Button
1x Buzzer
1x DS18B20 Temperature Sensor
1x 4k7? Resistor
Prerequisites:
Latest version of Rasbian installed on your SD Card
Raspberry Pi setup with a keyboard, mouse and monitor

1. First we need to enable I2C on our Raspberry Pi. We do this by opening
the raspi-config menu.
sudo raspi-config

2. We then need to go to the Interfacing Options menu.

3. Select I2C and then Yes to enable it.

4. Next we need to enable the 1-wire I2C library. To do this we need to edit the boot config.txt file
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
5. Scroll down to the bottom of the file and add the following line:
dtoverlay=w1-gpio

6. Now reboot
sudo reboot
7. Change the current directory to our gpio_python_code directory:
cd gpio_python_code
8. Create a file for our temperature script:
touch 7_temperature.py

9. Edit the 7_temperature.py script using nano 7_temperature.py and add the following code:
#!/usr/bin/python
import glob
from time import sleep
base_dir = '/sys/bus/w1/devices/'
device_folder = glob.glob(base_dir + '28*')[0]
device_file = device_folder + '/w1_slave'
def read_temp_raw():
f = open(device_file, 'r')
lines = f.readlines()
f.close()
return lines
def read_temp():
lines = read_temp_raw()
while lines[0].strip()[-3:] != 'YES':
sleep(0.2)
lines = read_temp_raw()
equals_pos = lines[1].find('t=')
if equals_pos != -1:
temp_string = lines[1][equals_pos+2:]
temp_c = float(temp_string) / 1000.0
temp_f = temp_c * 9.0 / 5.0 + 32.0
return temp_c, temp_f
while True:
print(read_temp())
sleep(1)

10. Execute your 7_temperature.py script
sudo python 7_temperature.py