Login / Signup
Cart
Your cart is empty
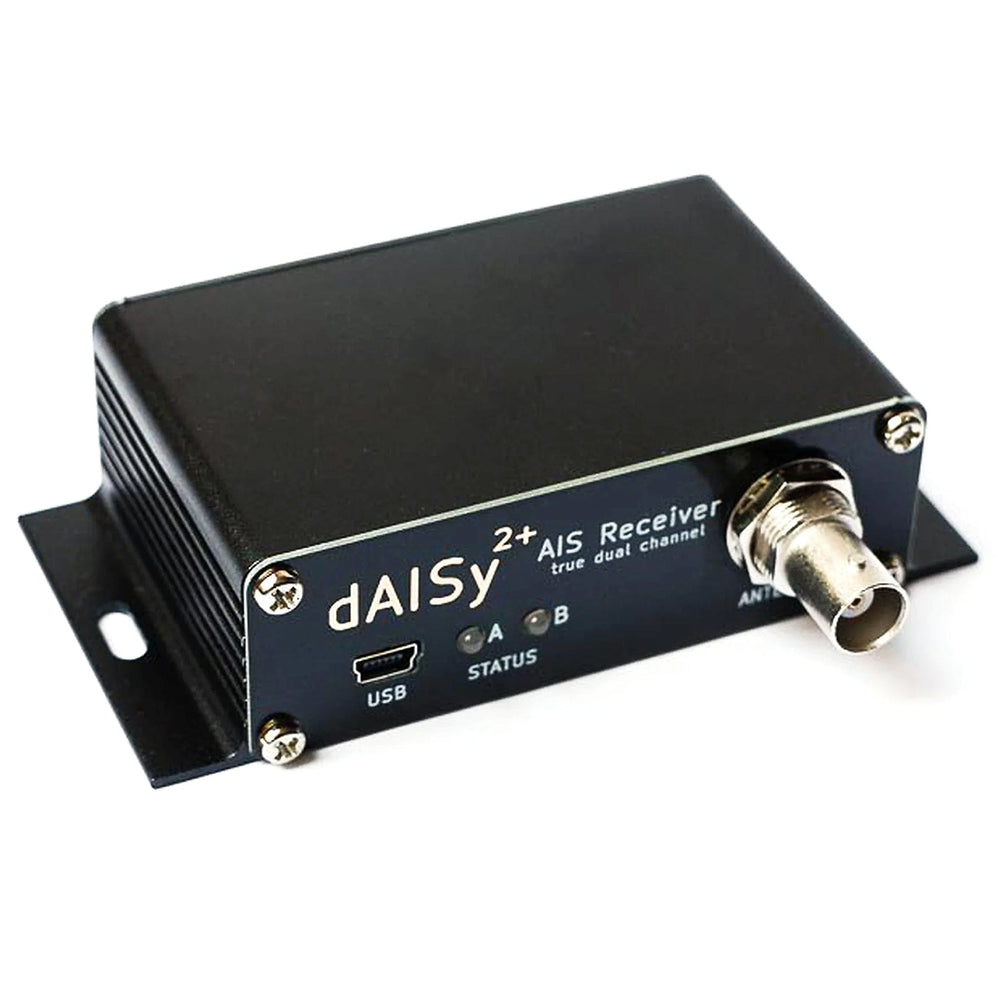
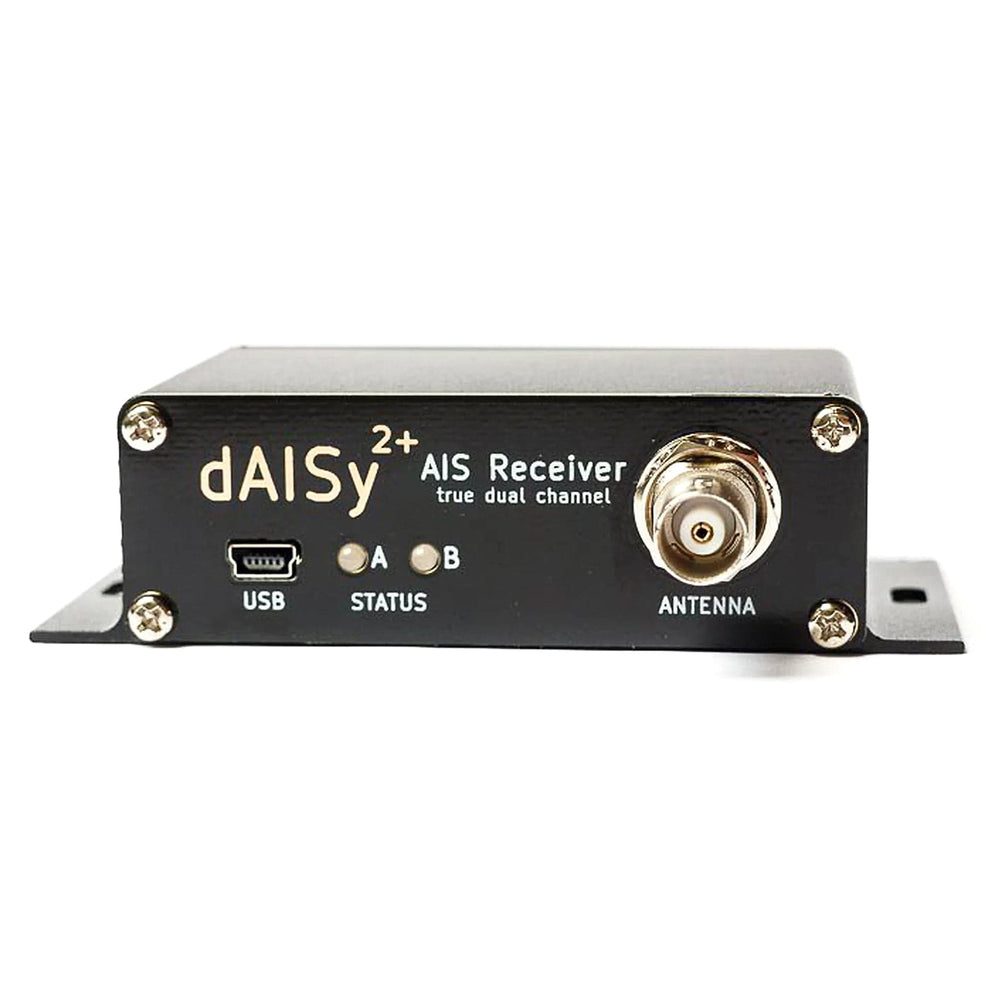



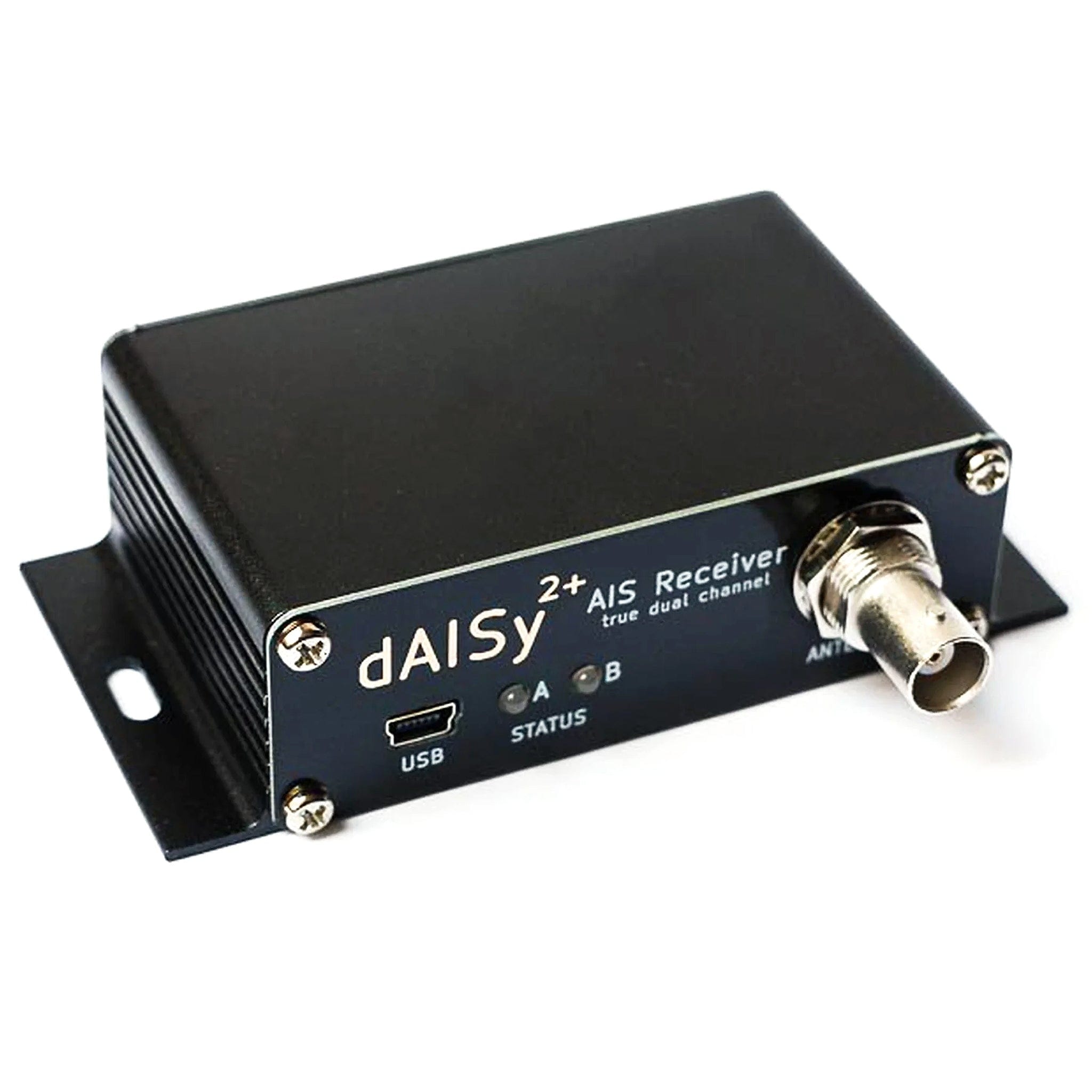
Following the popular dAISy HAT for the Raspberry Pi, due to popular demand, we're now stocking the Wegmatt dAISY 2+ AIS receiver!
This AIS receiver is built for boaters. Compact, robust, and with all the interfaces you need. Thanks to its two-channel design, the dAISy 2+ receives about 40% more messages than the original single-channel dAISy. This improves acquisition time and update rate of AIS targets, while the range is comparable for both models.
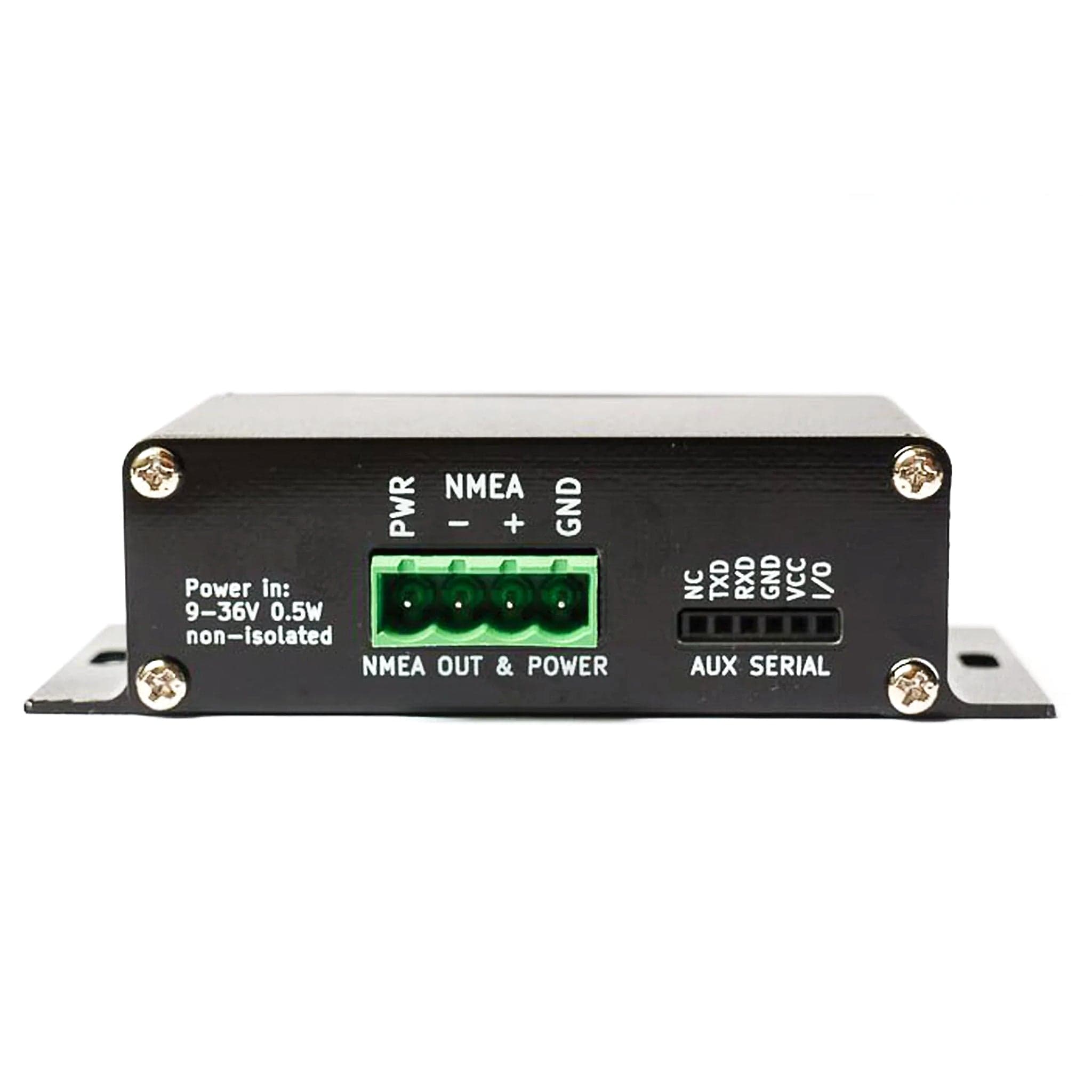
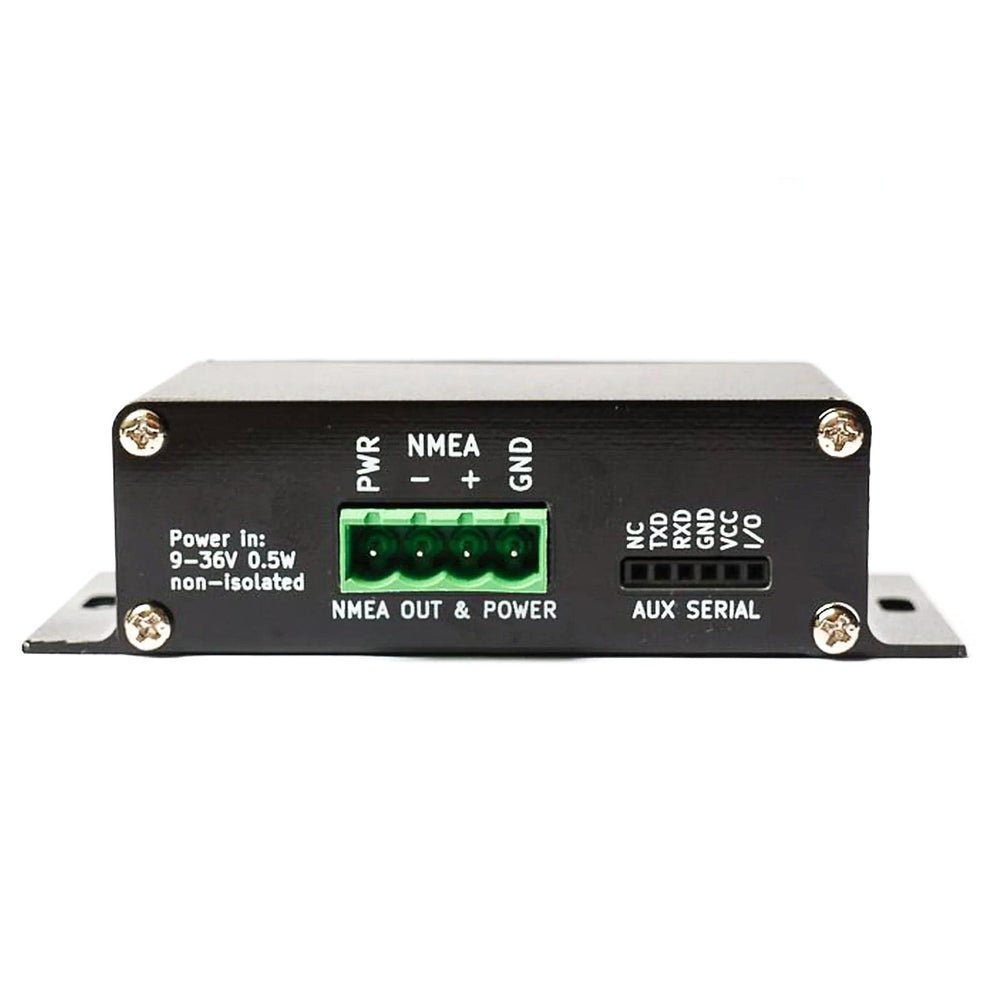
The dAISy 2+ AIS Receiver can directly talk to chart plotters and other marine electronics. In addition, the integrated DC/DC converter allows you to power it from your boat's 12-36V power system, removing the need for a USB power source.
dAISy was successfully tested with chart plotters (Garmin GpsMap 750s, Standard Horizon CP180i, Samyung N700), NMEA routers (vyacht) and RS-422 routers (Transas 4 port RS-422 to Ethernet). I expect it to also work with other devices that support NMEA 0183 or RS-422 input.
OpenCPN, an open-source chart plotter and navigation software, can be used with devices like dAISy to track ships on a map. Any software running on a PC, Mac or small Linux computer that accepts AIS data from a serial input will work with dAISy.
Several of our customers built chart plotters based on a Raspberry Pi 2, OpenCPN and dAISy. A detailed write-up can be found here.
Disclaimer: WE DO NOT RECOMMEND relying solely on dAISy for navigation and collision avoidance!
dAISy is well suited to report nearby ship traffic to websites and services like MarineTraffic, FleetMon, AISHub or Pocket Mariner.
A user of an early prototype of dAISy documented how to configure a Linux system like Raspberry Pi to report directly to MarineTraffic here.
An alternative approach is to use Kplex. Kplex is a NMEA-0183 Multiplexer which allows to feed the AIS data stream to multiple targets, including services like MarineTraffic and AISHub. Kplex also allows you to setup a NMEA server to distribute AIS to other devices on your network, like for example via WiFi to a navigation app running on an iPad. MUPLEX for Linux and NMEA Router for Windows are a similar tools.
For tinkerers, the serial data stream is available on a 0.1" header on the back of the unit. Advanced users can combine dAISy with a Bluetooth module to receive AIS on wireless devices, or connect a data logger like SparkFun OpenLog.
In fact, the pin-out of the auxiliary serial port is compatible with the HC-05/HC-06 Bluetooth modules and DT-06 TTL to WiFi modules commonly found on eBay, AliExpress and the like. Here are instructions for configuring the WiFi module.
If UART serial communication is all you need, also take a look at our dAISy HAT, which can be run standalone without a Raspberry Pi.
With our open-source work, we pioneered a new category of AIS receivers designed around the SiLabs EZRadioPro single chip radio IC. This architecture is instrumental for the very low price, small form factor and low power consumption. The trade-offs are longer acquisition time, lower sensitivity and less range than traditional AIS receivers.
Field tests with conventional dual-channel receivers (like SmartRadio SR162, advanSEA RX-100) showed that dAISy 2+ indeed has lower range and is slower to acquire targets. However dAISy 2+ clearly outperforms other low-cost receivers that we've tested (Quark-elec, MarineGadget).
Our observation is, that with a good antenna dAISy is well-suited to monitor local ship traffic. If you need maximum performance and are willing to pay for it, go with a receiver from the established brands.