Login / Signup
Cart
Your cart is empty
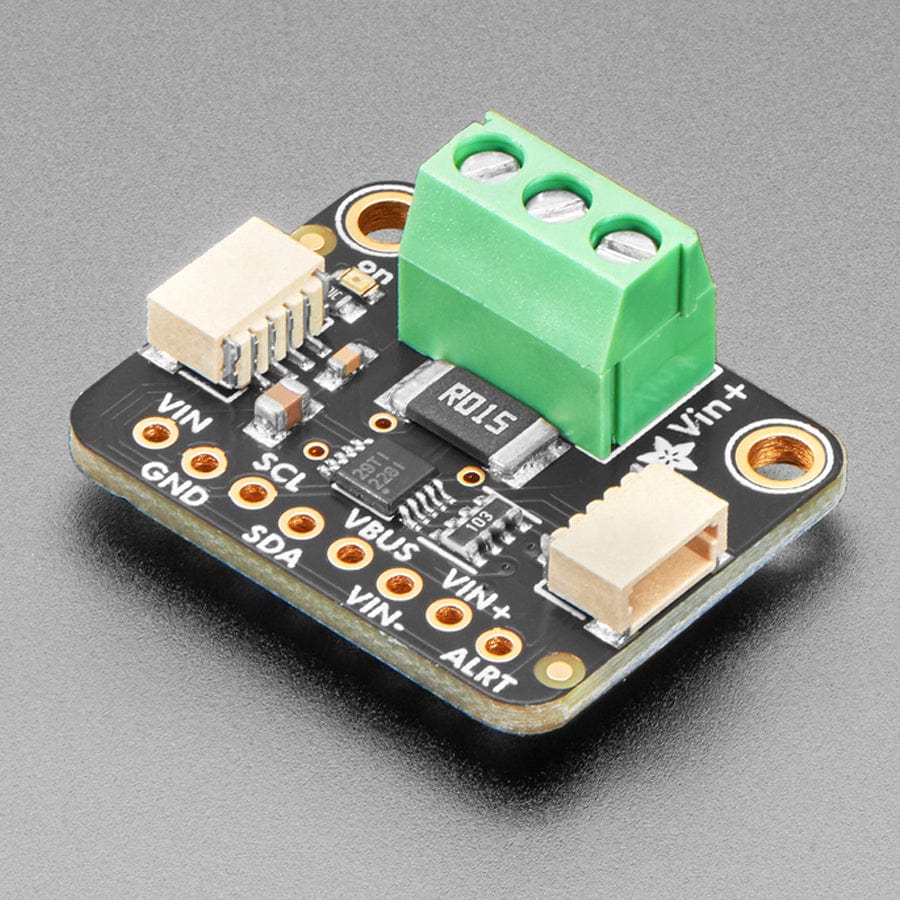
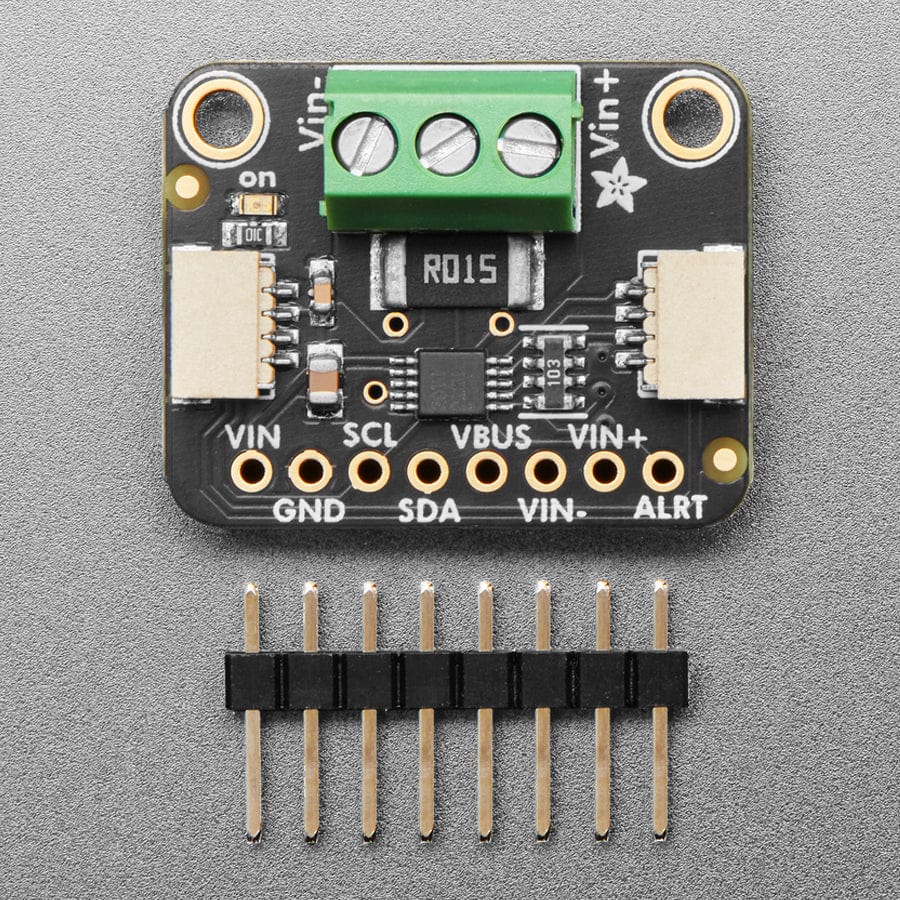
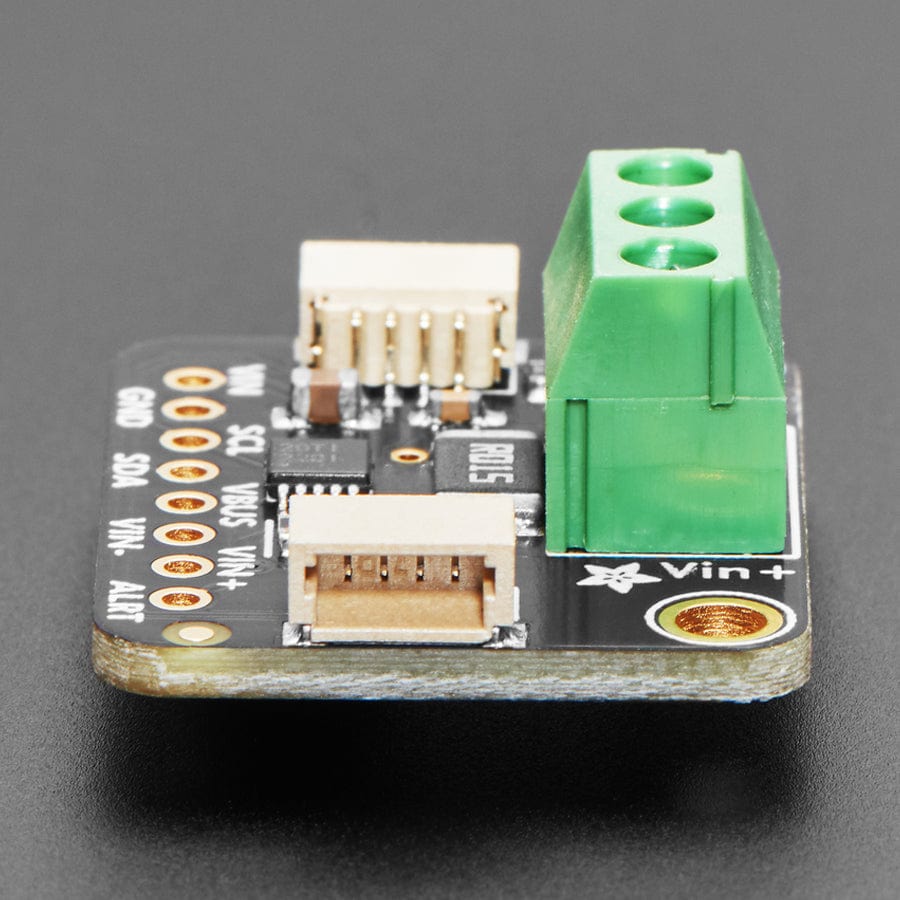
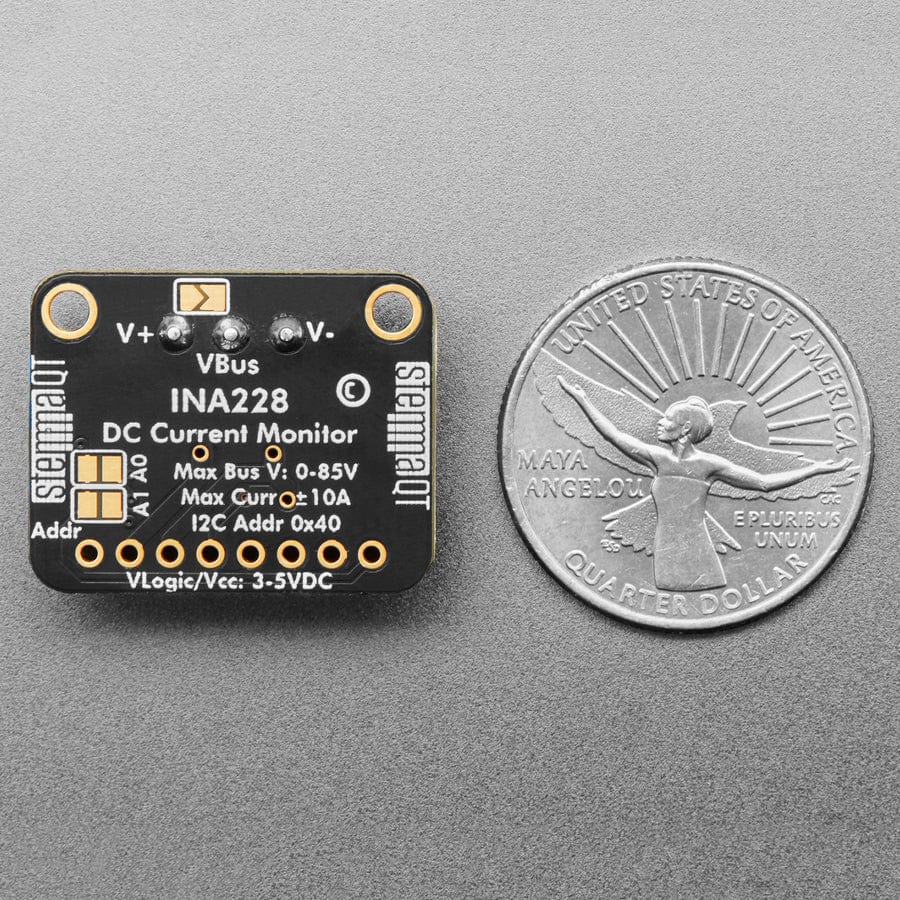
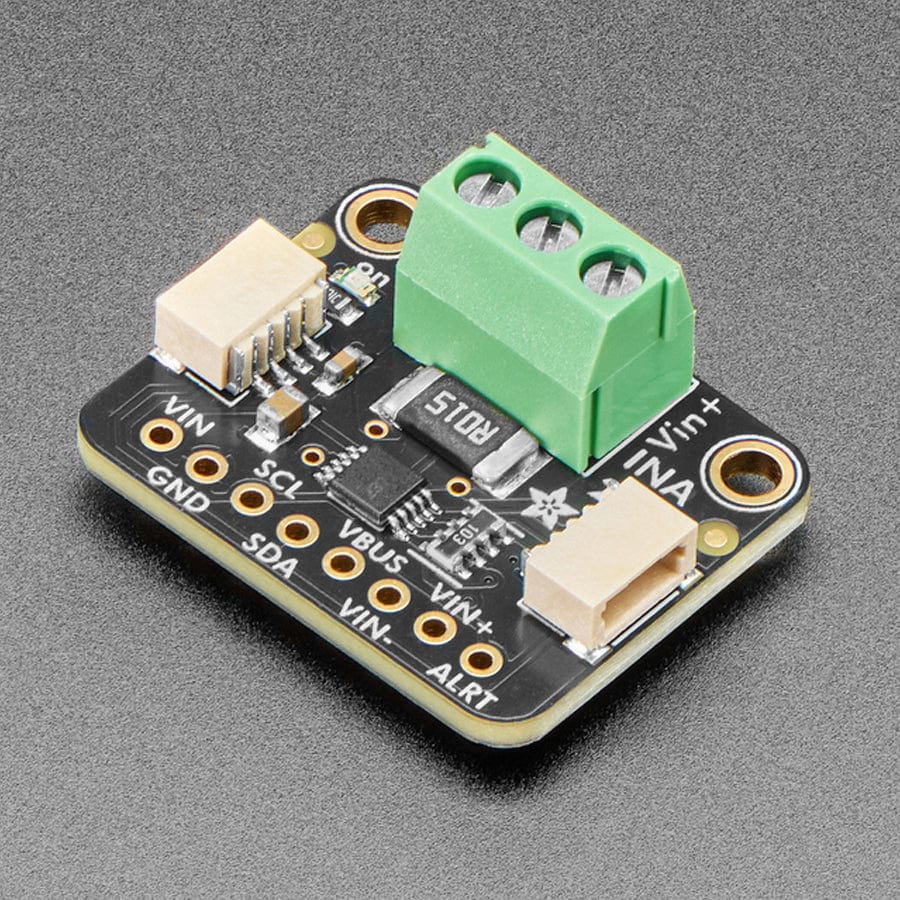
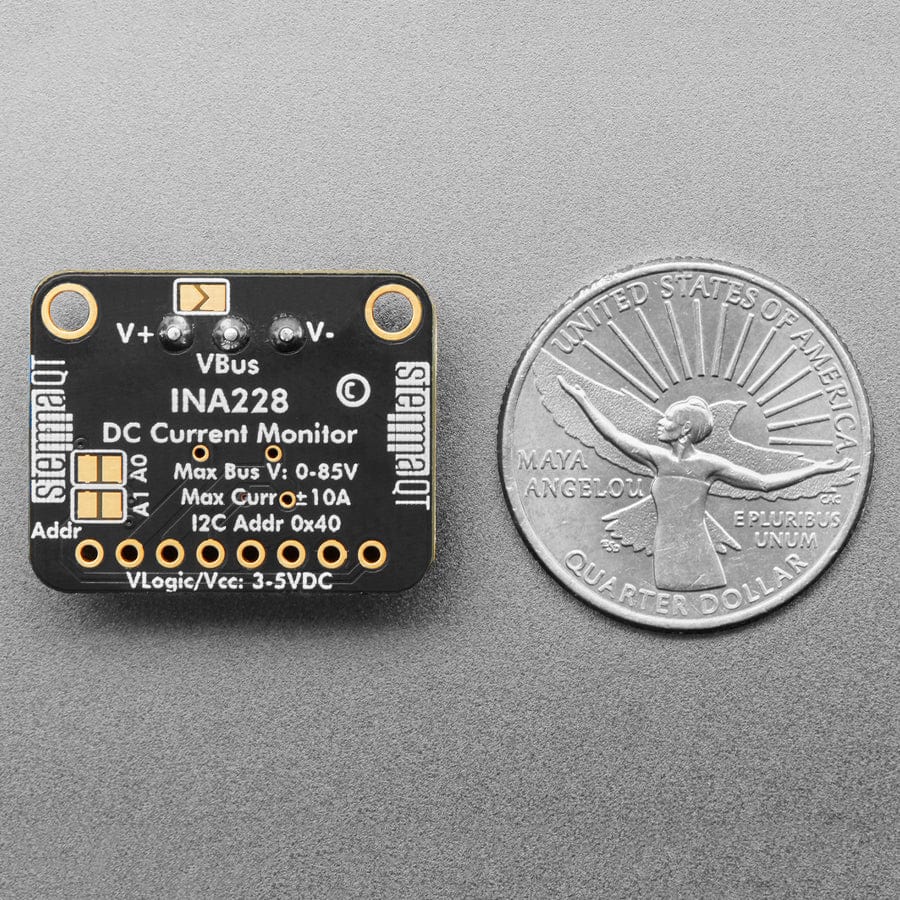
The INA228 is an amazing power monitoring chip, with best-of-everything support: up to 85VDC common-mode, high or low side measurements, 20-bit (!) ADC for precision measurements from milliamp to Amp, and I2C interface for easy configuration of alerts, oversampling, gain adjustments and more!
This breakout board may well be the last current sensing solution you ever need to buy. Not only can it do the work of two multimeters, but it can do it with amazing precision and flexibility. With it you can measure high or low side DC current, the bus voltage, and have it automatically calculate the power. It can do so over impressive voltage, current, and temperature ranges with better than 1% accuracy, all while delivering the data in an easy-to-use format over I2C.
Works great with any microcontroller that is CircuitPython or Arduino compatible as well as single-board computers such as the Raspberry Pi. It is compatible with 3V or 5V logic and can measure bus voltages up to +85VDC. Not for use with AC voltages.
Most current measuring devices operate with some notable constraints that limit what they can be used for. Many are low-side only which can cause issues as the ground reference changes with current. Others like its little sister the INA219B avoid this by measuring on the high side but need to change their shunt resistor to measure different current ranges. The INA228 avoids these limitations, and with the precision 15milliohm shunt resistor on board, it can be used to measure as much as +85V at up to 10A (~10uA per LSB) or 2.75A (~2.5uA per LSB) Continuous on either the high or low side.
The voltage across the integrated 15 milliohms (.015 ohms!), 0.1% shunt resistor is measured by the internal 20-bit ADC, allowing for measurements over the impressive current range with a resolution of 10uA per LSB in high current measurement mode or 2.5uA per LSB in low current measurement mode.
In a high-side configuration, the bus voltage measurement and power calculation can be retrieved accurately, however advanced hackers wanting to measure bus voltage in a low-side configuration will need to cut the jumper connecting V+ to VBUS and connect the VBUS pin to the voltage bus.
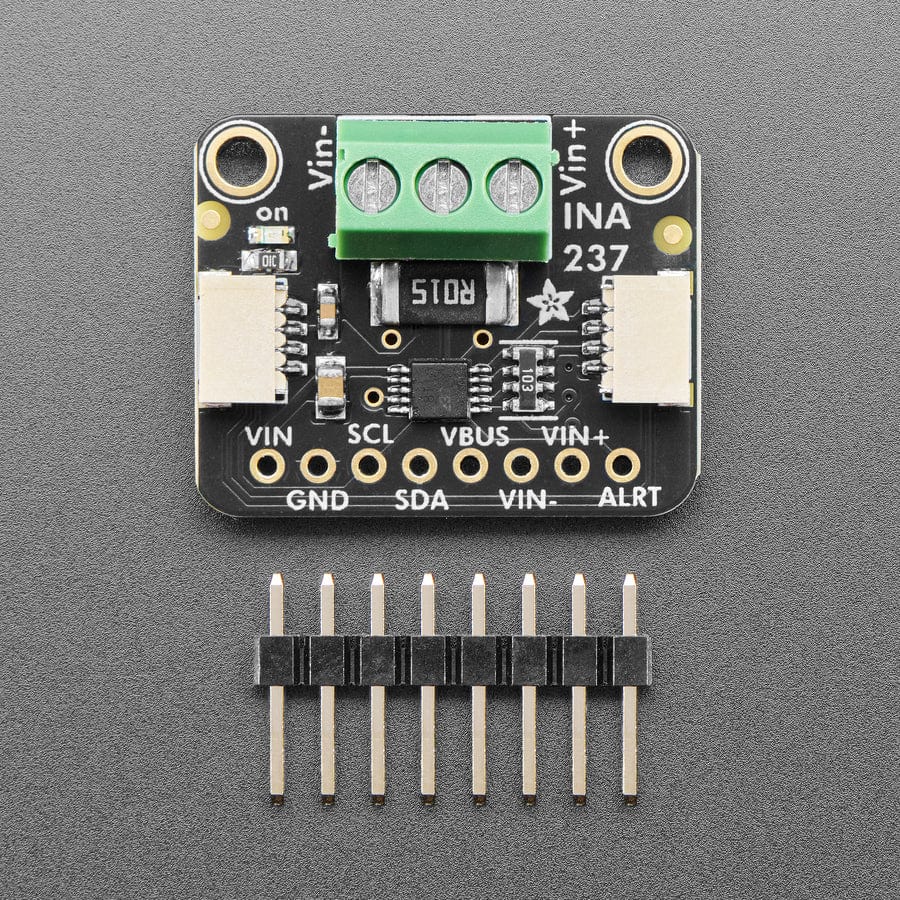
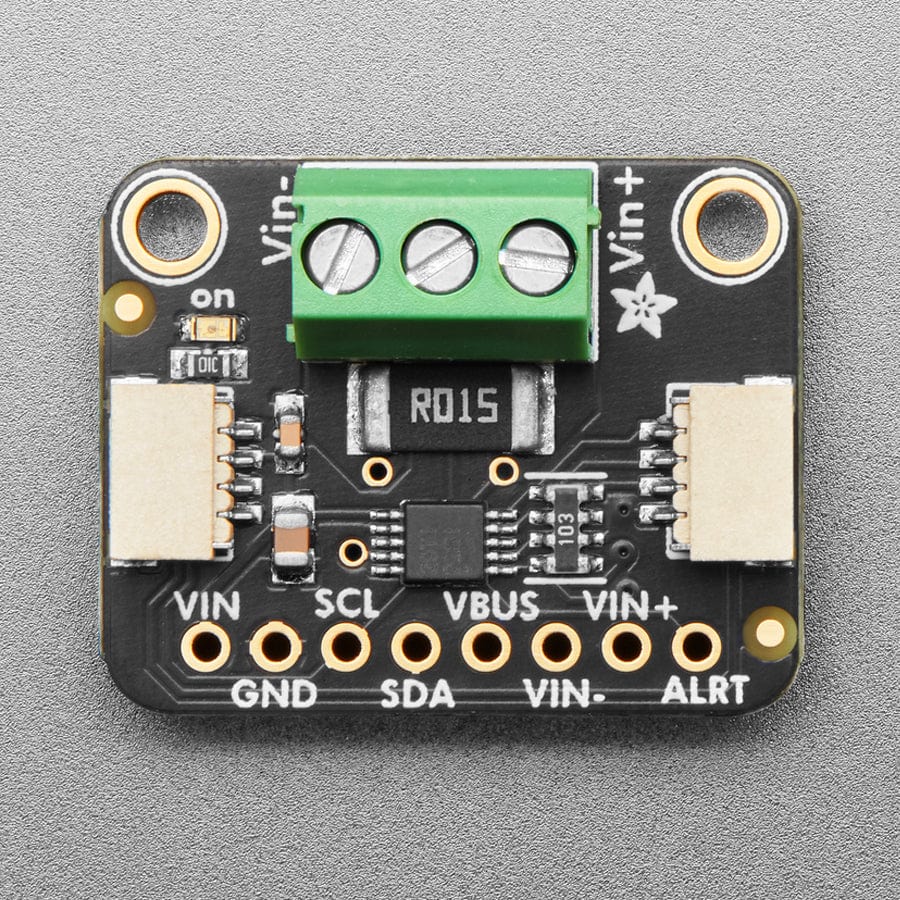
Comes as a fully assembled breakout board with a 3.5mm terminal block and header. Some light soldering is required to attach the header for use in a breadboard.