Login / Signup
Cart
Your cart is empty
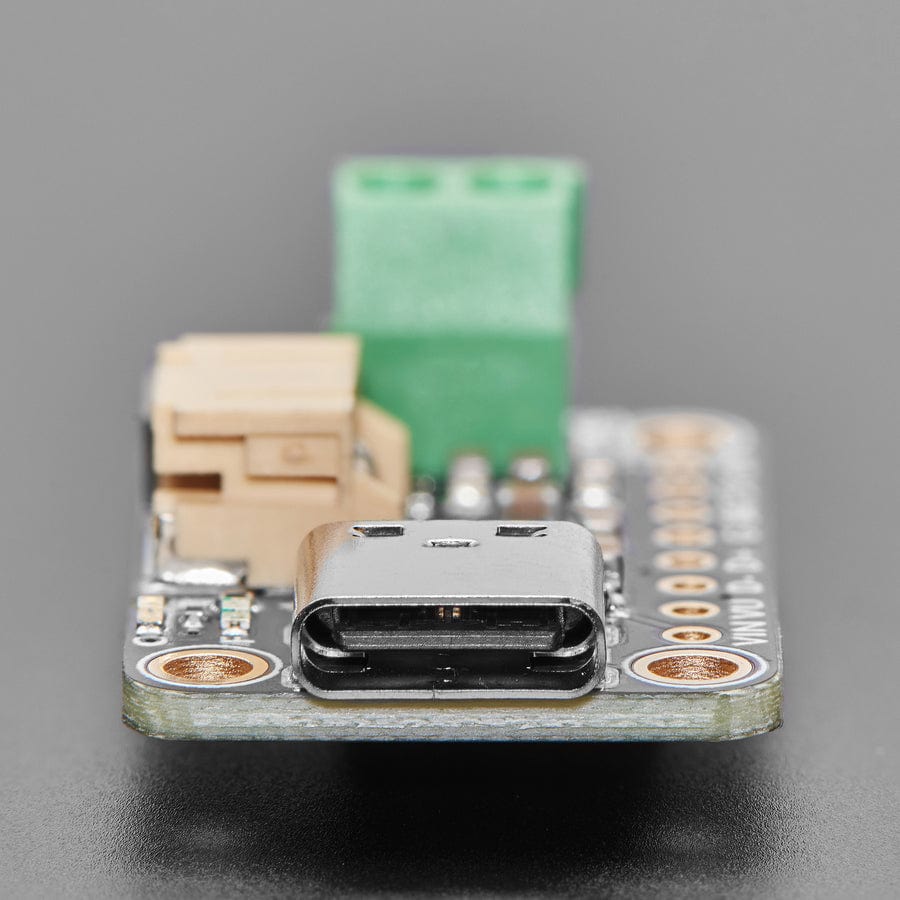
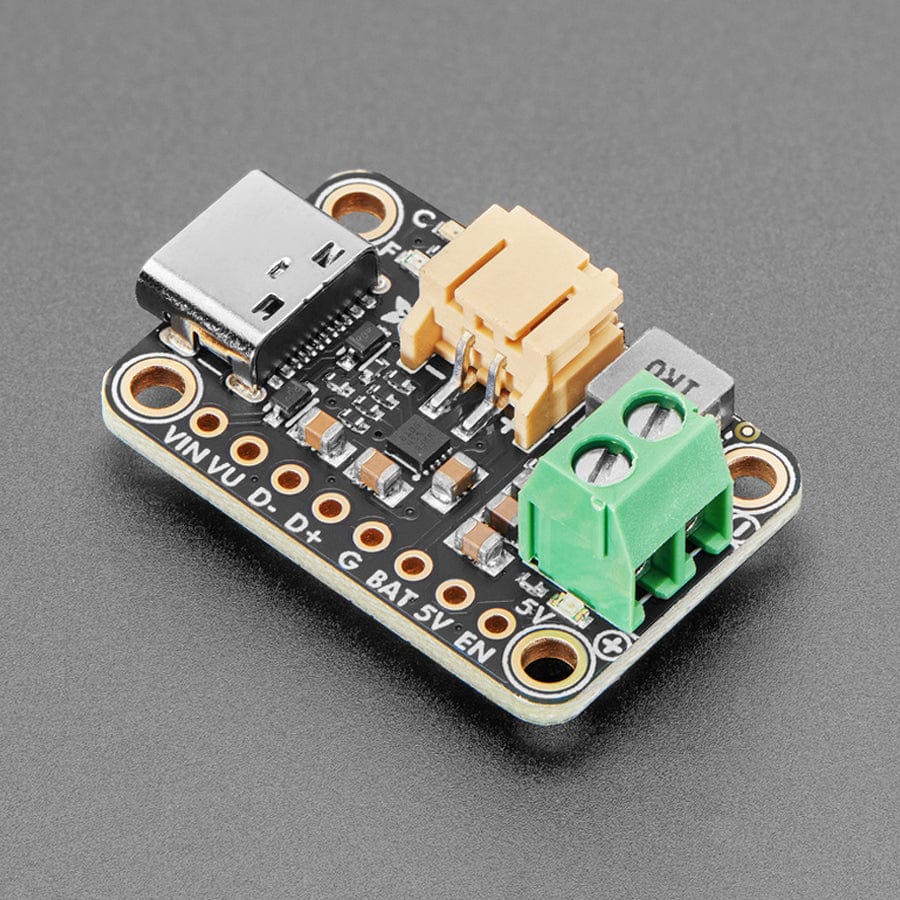
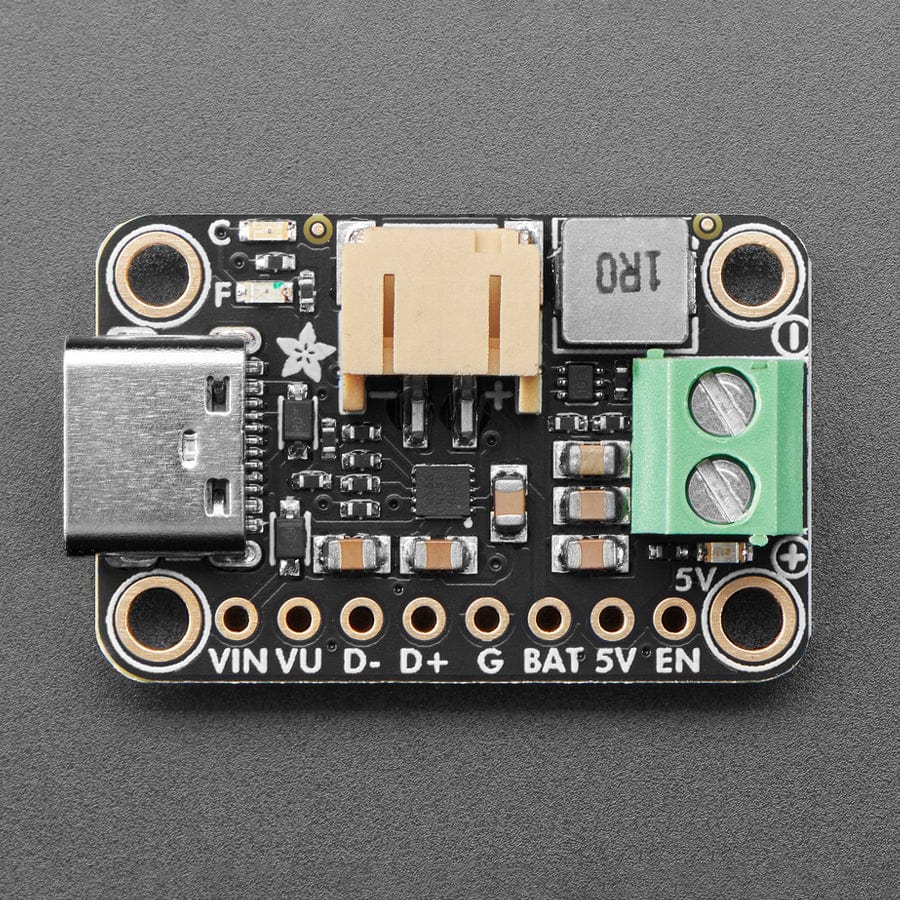
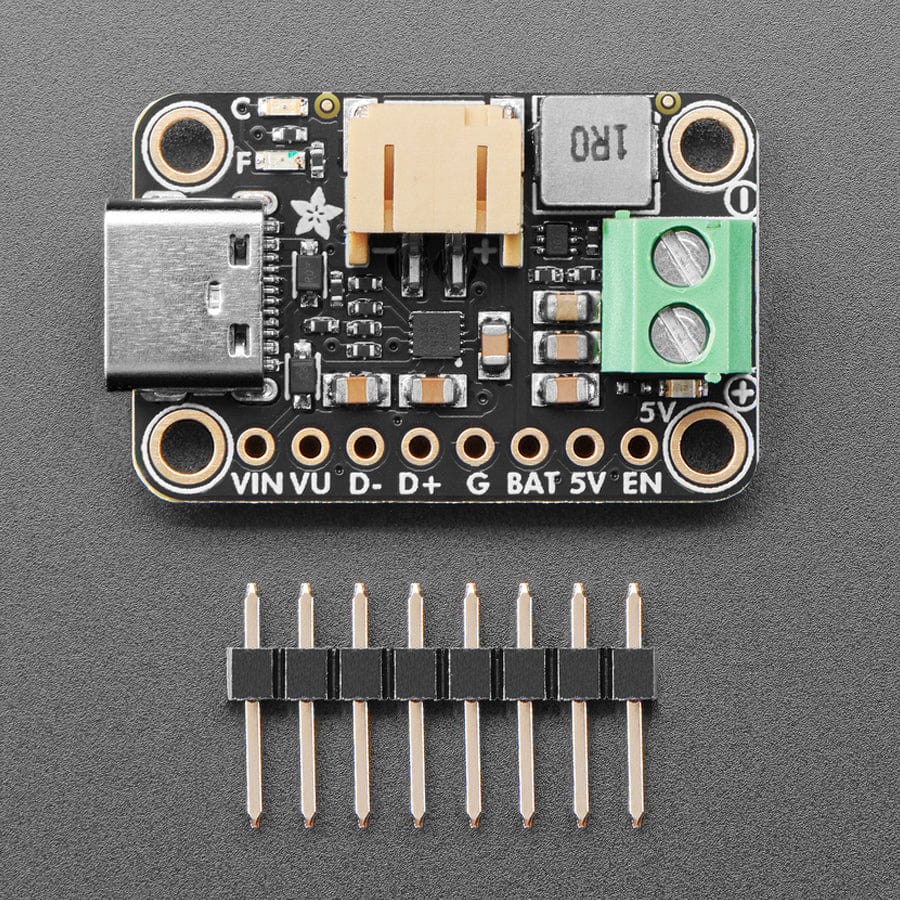
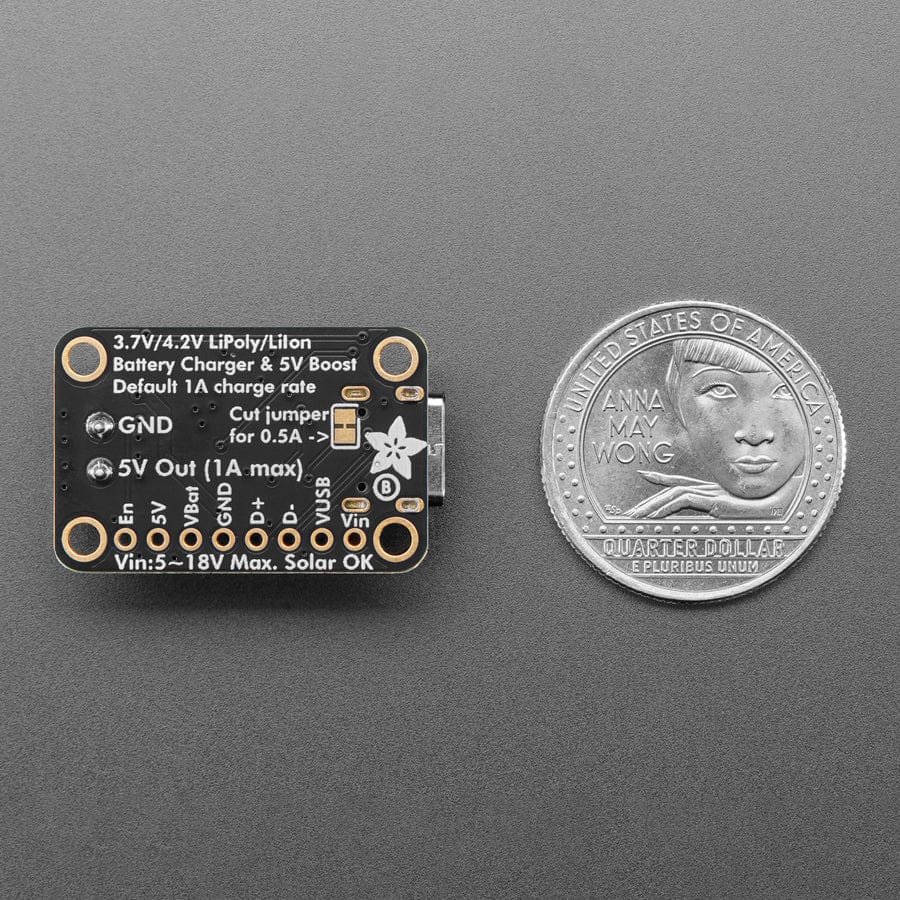
We're always on the lookout for better ways to make projects portable: being able to charge your battery in the most convenient manner will let projects run no matter what power is available. Then we added a power supply chip with it to let you run your project without a separate board. The result is the Adafruit bq25185 USB / DC / Solar Charger with a 5V Boost Board!
It uses the new bq25185 is a nifty charger chip with fairly high charge current, power path support, and the ability to charge from USB, DC or solar power. It's also a great value, so it's a good upgrade from MCP73833 or MCP73831-based charger boards. The boost converter is the TPS61023, which will give up to 1 Amp output with good efficiency, to squeeze the most power possible out of your battery.
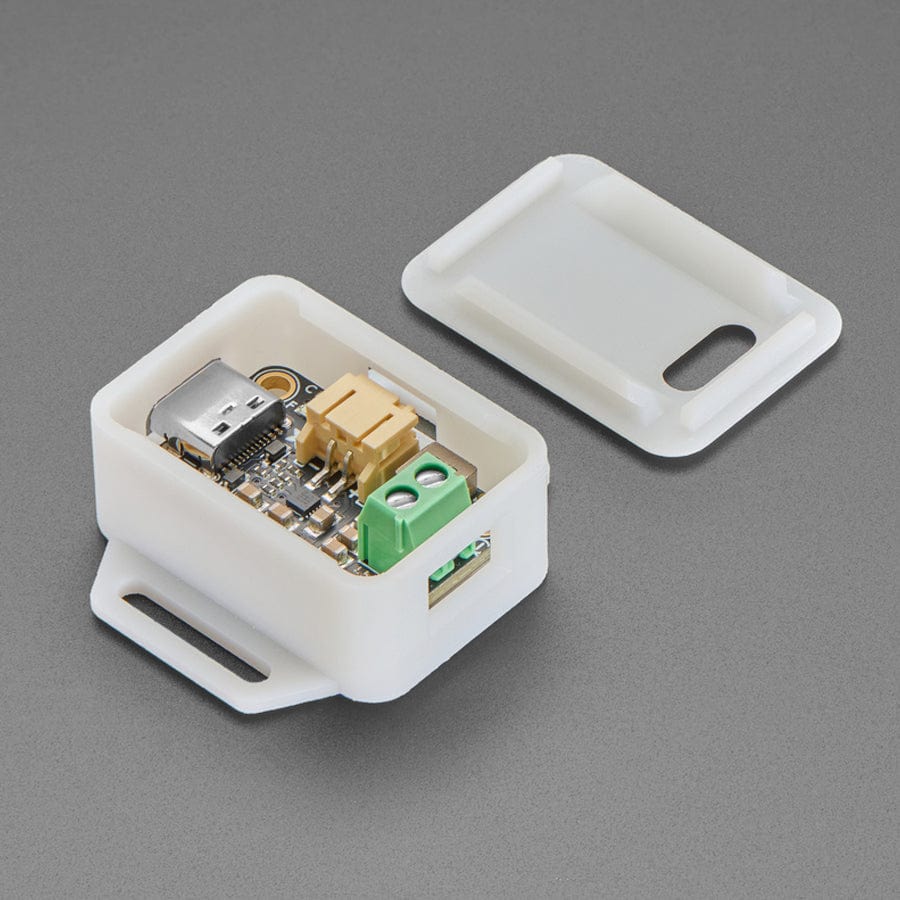
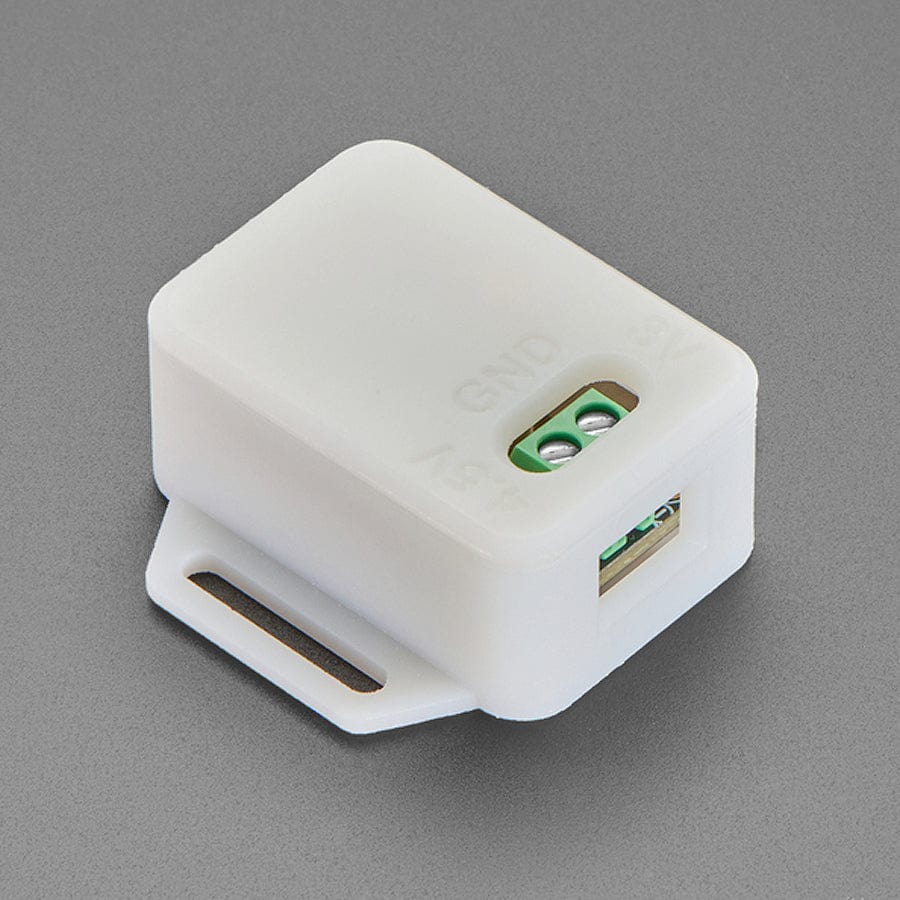
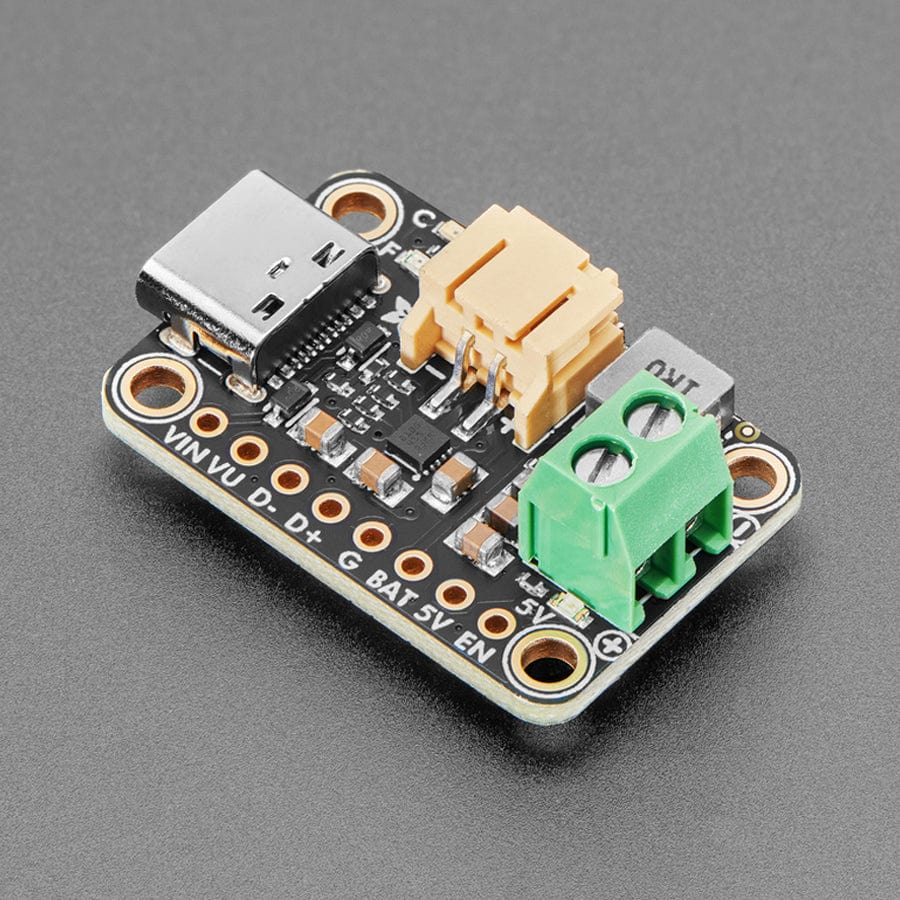
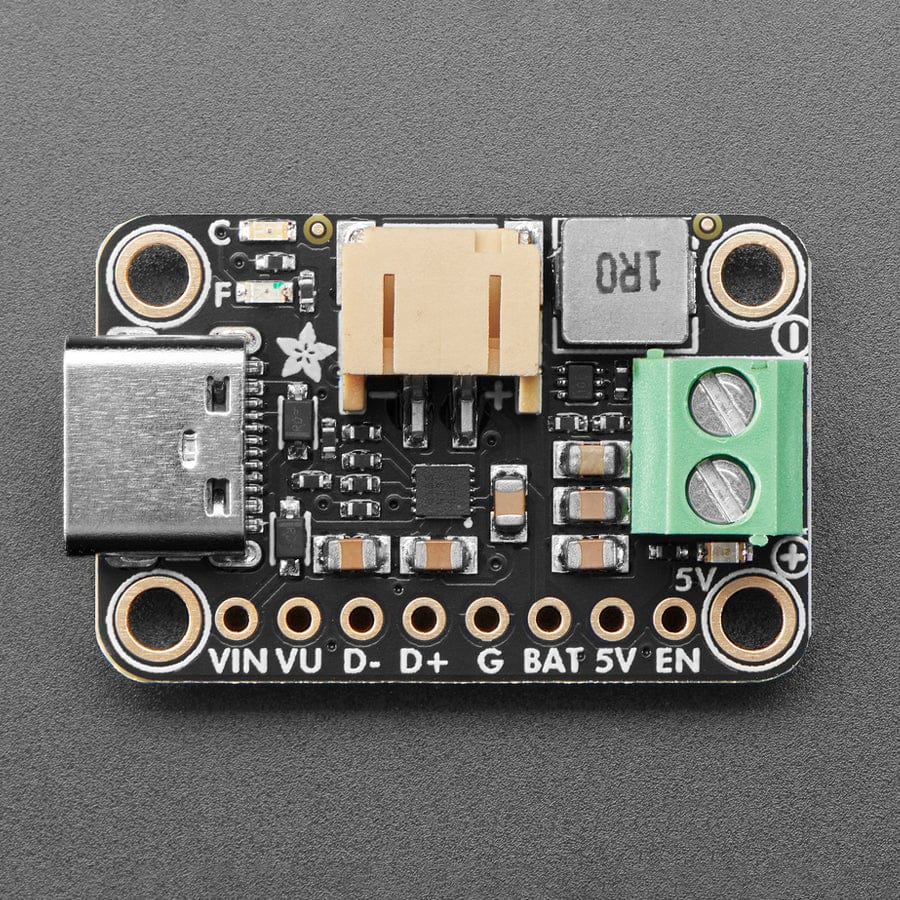
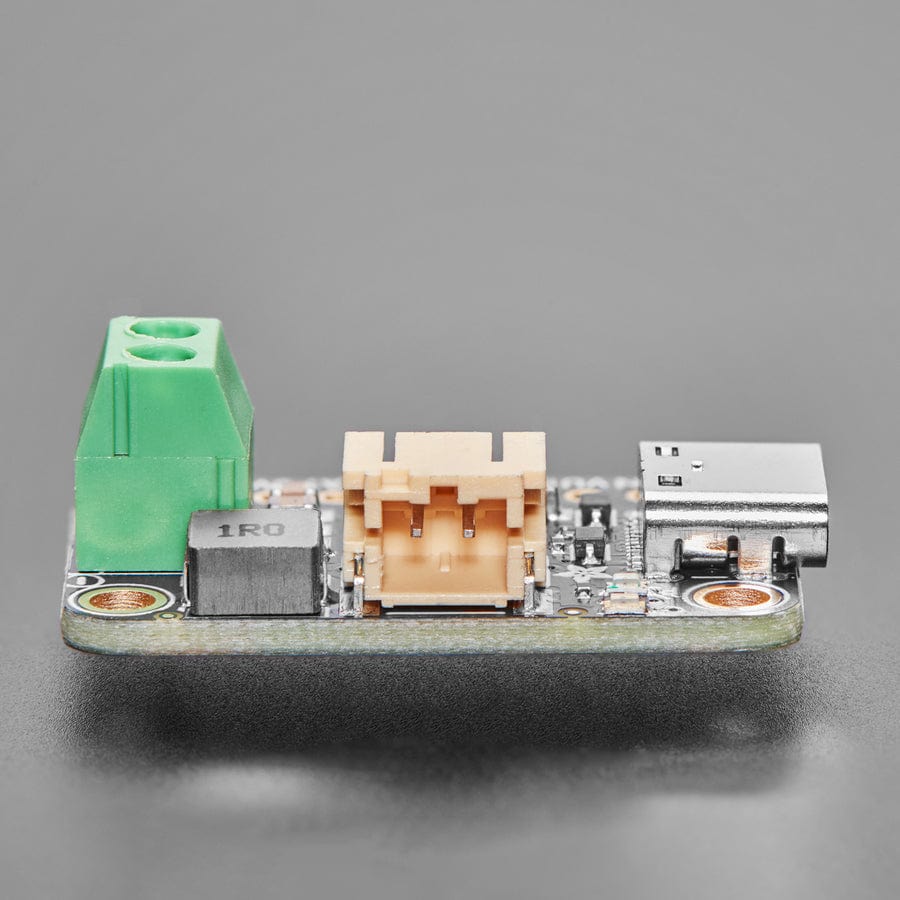
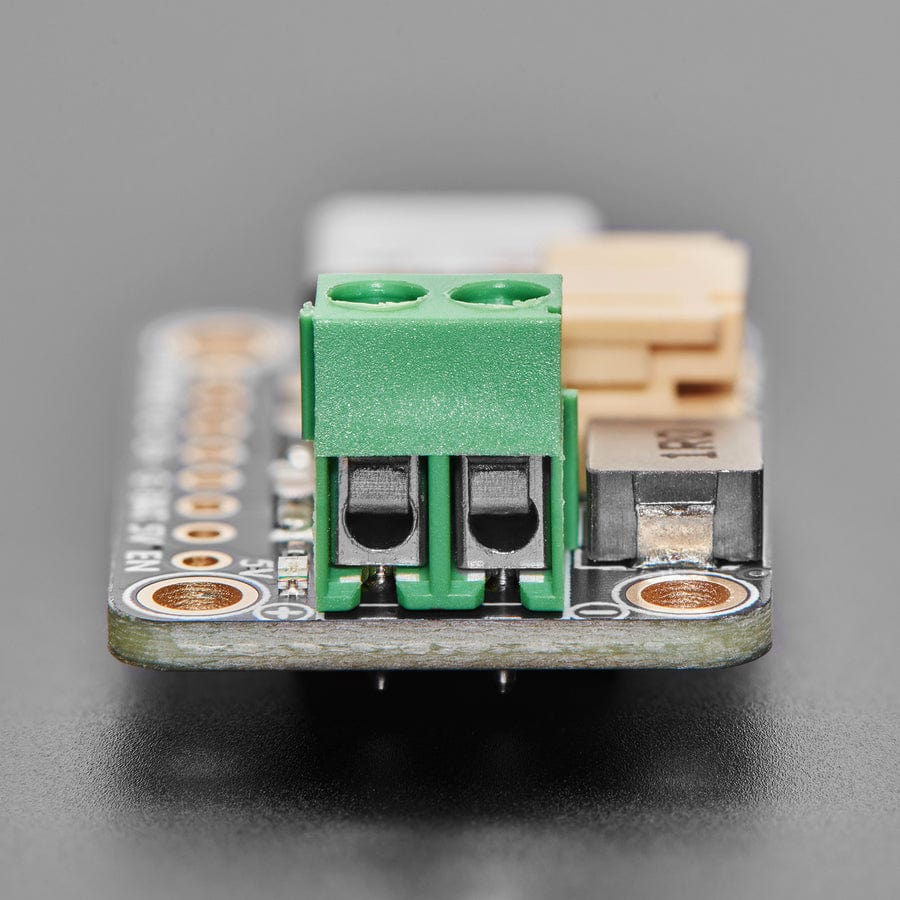
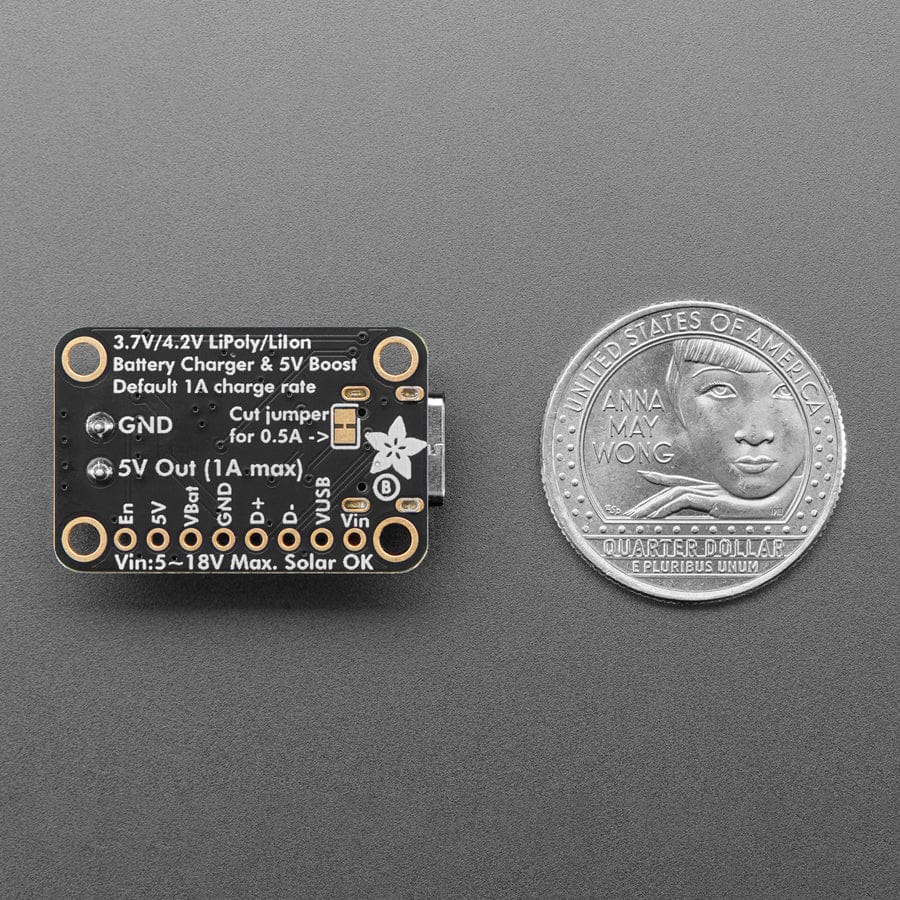
This board is meant to be everything you need to power your 5V electronics: simply connect a 500mAh or larger battery to the JST PH 2-pin port, then charge it when you can from USB or DC/solar. At the other end is a terminal block which will provide the 5V output from the boost converter.
If you're looking for a case, click here to find a tailor-made one in our shop
This board is pretty much plug-and-play. Change the charging jumper if you like, then connect your battery to the BATT port, and the 5V output goes to your circuit. You can monitor the voltage on the battery via the secondary pads on the bottom edge, if necessary.
To use with solar, pick up a 5~7V solar panel (using a higher voltage panel will only lose the extra voltage as heat so there's no benefit to going over 7V), and either cut the connector off to wire it directly, or use a 2.1mm adapter cable plus a 2.1mm terminal block to get two wires for the DC Input port.
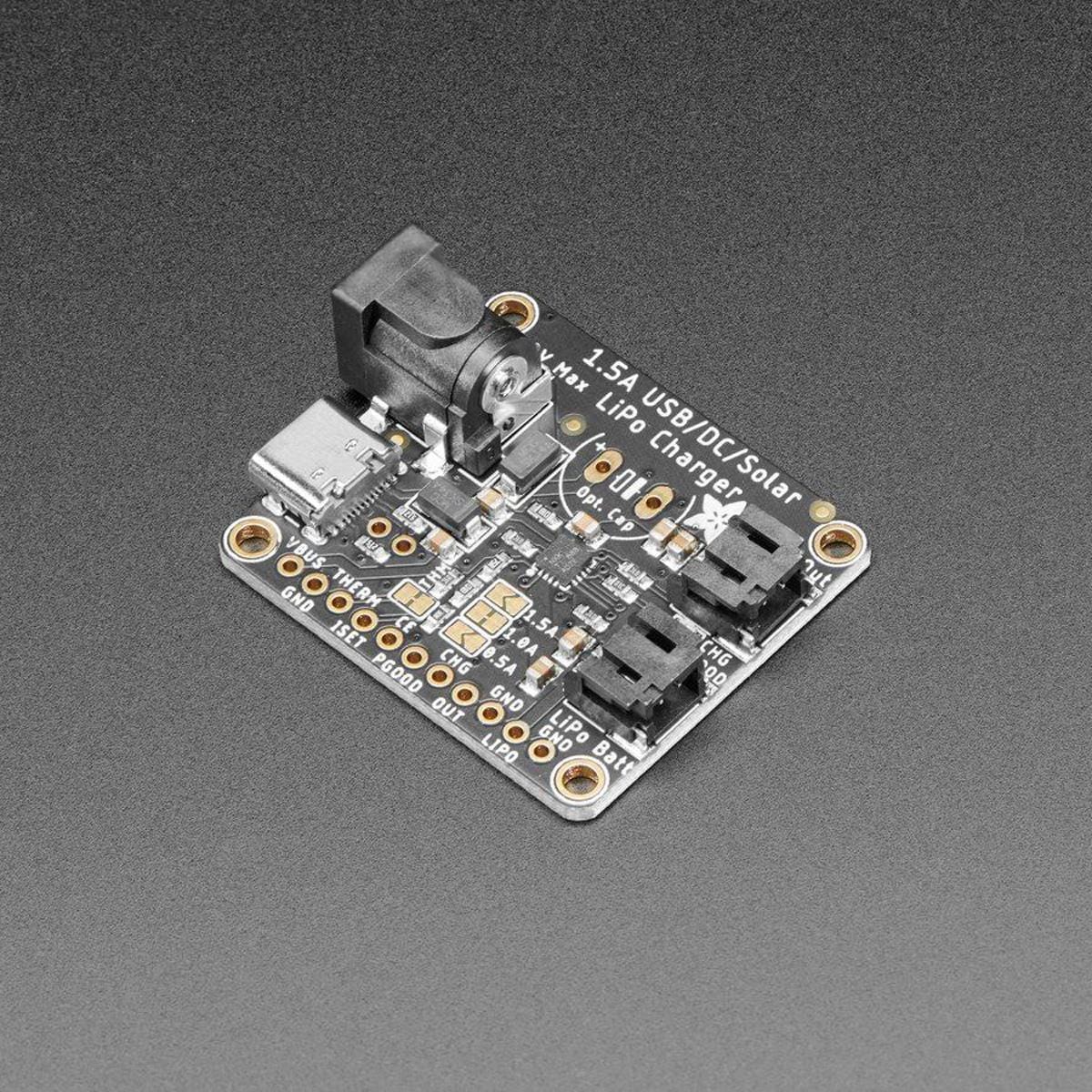
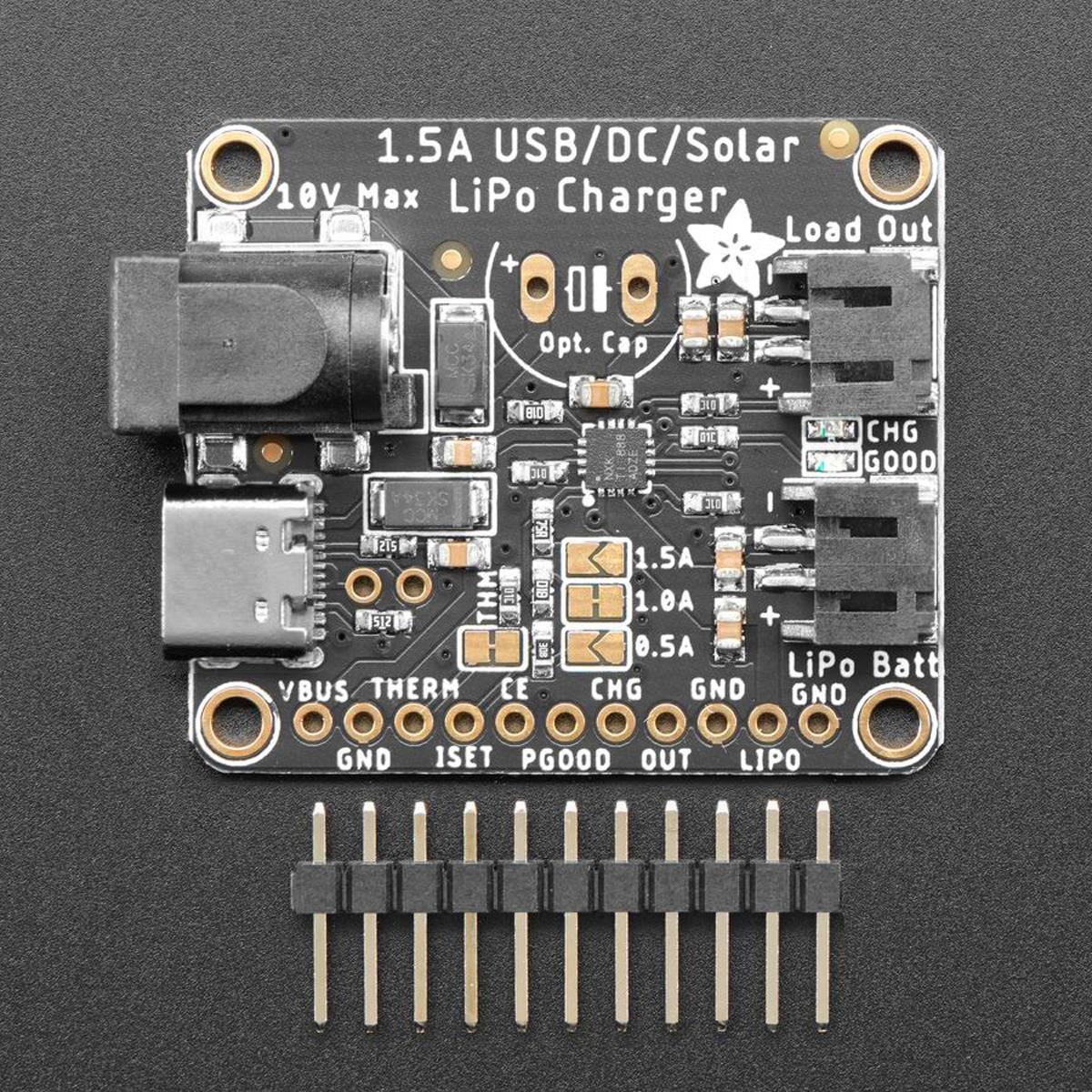
If you need a board with a higher charge current or a DC plug already on board, check out the bq24074 which has up to a 1.5A charge rate and an on-board 2.1mm DC jack. It doesn't have a boost converter but you could wire up the TPS61023 separately.